Coronary artery disease (CAD), also known as coronary heart disease or atherosclerotic heart disease, is a common condition that occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked by a buildup of plaque. This can lead to reduced blood flow to the heart and cause chest pain or discomfort (angina), heart attacks, and other heart-related problems. Here are some signs and symptoms of CAD and tips for protecting your heart:
Signs and Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease:
Chest Pain (Angina): This is the most common symptom. It can feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the chest. It may also radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder, or back.
Shortness of Breath: You may experience difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or when lying down.
Fatigue: Unexplained fatigue or weakness can be a sign of reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
Heart Attack: Sudden, intense chest pain, along with symptoms like shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, and lightheadedness, can indicate a heart attack.
Irregular Heartbeat: Arrhythmias or palpitations can be a sign of CAD.
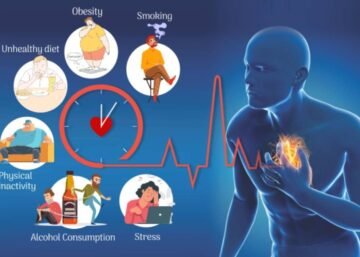
Tips for Protecting Your Heart and Reducing the Risk of CAD:
Healthy Diet: Consume a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy products. Limit saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a risk factor for CAD. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is essential.
Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for CAD. If you smoke, seek help to quit, as it will greatly reduce your risk.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or hobbies you enjoy.
Limit Alcohol: If you choose to drink, do so in moderation. For most people, this means up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
Control Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for CAD. Regularly monitor your blood pressure, and if it’s high, work with your healthcare provider to manage it.
Manage Cholesterol: Keep your cholesterol levels in check by eating a heart-healthy diet and, if necessary, taking medication as prescribed by your doctor.
Diabetes Control: If you have diabetes, it’s crucial to manage your blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of CAD.
Regular Check-ups: Visit your healthcare provider for regular check-ups and screenings to assess your heart health and detect any issues early.
Medications: If prescribed, take medications for CAD, high blood pressure, or other related conditions as directed by your healthcare provider.
Remember that genetics can also play a role in CAD, so it’s essential to be aware of your family history and discuss it with your healthcare provider. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and working with your doctor to manage risk factors, you can reduce your risk of coronary artery disease and maintain good heart health
Lifestyle Changes: If you have been diagnosed with CAD, follow your doctor’s recommendations for lifestyle changes and medications.