Cardiomyopathy is a medical term that refers to a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle, leading to its structural and functional abnormalities. These conditions can make it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently and can lead to various heart-related problems. There are several types of Cardiomyopathy, including:
Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM): This is the most common type of Cardiomyopathy. In DCM, the heart muscle becomes weakened and stretched (dilated), which reduces its ability to pump blood effectively. This can lead to heart failure and other complications.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM): HCM is characterized by abnormal thickening (hypertrophy) of the heart muscle, particularly the left ventricle. This can obstruct blood flow out of the heart and may lead to symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and an increased risk of arrhythmias.
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: In this type, the heart muscle becomes stiff and less elastic, making it difficult for the heart to fill with blood between beats. This can lead to heart failure and other problems.
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC): ARVC is characterized by the replacement of heart muscle with fat and fibrous tissue, primarily in the right ventricle. This can increase the risk of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
Unclassified Cardiomyopathy: Some cases of cardiomyopathy do not fit neatly into one of the above categories, and they are categorized as unclassified or “other” types.
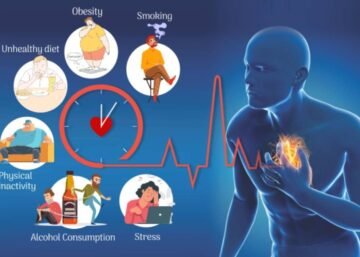
The exact cause of Cardiomyopathy can vary depending on the type but may include genetic factors, viral infections, autoimmune conditions, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications or toxins. Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy can range from mild to severe and may include fatigue, swelling of the legs and ankles, breathlessness, chest pain, and palpitations. Treatment typically focuses on managing symptoms, slowing the progression of the disease, and addressing underlying causes.
This may involve lifestyle changes, medications, medical devices (such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators), or, in severe cases, heart transplantation. It is important for individuals with Cardiomyopathy to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan.