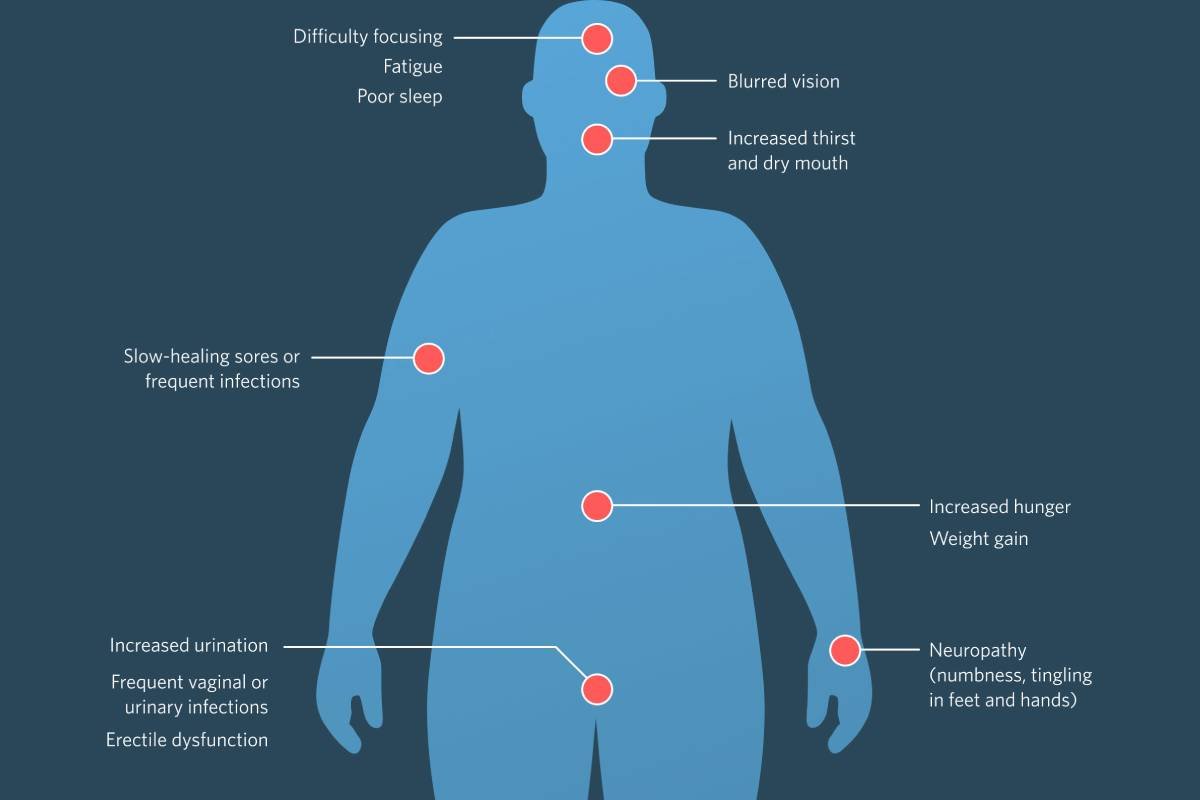
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body metabolizes glucose (sugar). It often develops slowly, and some people may not notice symptoms for years. Here are eight common signs and symptoms to look out for:
Frequent Urination (Polyuria): One of the most common early symptoms of type 2 diabetes is an increase in the frequency of urination. High blood sugar levels lead to excess glucose in the urine, which pulls more water from the body, causing increased urination.
Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia): As you urinate more frequently, you may become dehydrated, leading to increased thirst. This is your body’s way of trying to replenish the lost fluids.
Increased Hunger (Polyphagia): Even though people with type 2 diabetes are consuming more calories, their cells are not getting the energy they need due to insulin resistance. This can result in persistent hunger and overeating.
Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite an increase in appetite and food consumption, some people with type 2 diabetes experience unintentional weight loss. This occurs as the body starts breaking down fat and muscle for energy since glucose is not effectively entering the cells.
Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can lead to tiredness and general fatigue. The cells in your body may not be getting enough glucose for energy, which can leave you feeling drained.
Blurred Vision: Changes in blood sugar levels can affect the shape of the eye’s lens, leading to blurred vision. This symptom is usually temporary and improves with better blood sugar control.
Slow Wound Healing: High blood sugar can affect the body’s ability to heal itself. Wounds and sores may take longer to heal, and infections may be more common.
Frequent Infections: Type 2 diabetes can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, particularly skin and urinary tract infections.
It’s important to note that not everyone with type 2 diabetes will experience all of these symptoms, and some may have no noticeable symptoms at all. Regular check-ups and blood tests with a healthcare provider are crucial for diagnosing and managing type 2 diabetes. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis and effective management are essential for controlling type 2 diabetes and preventing complications.





